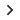In the complicated arena of clinical trials, data reigns supreme. The success of a trial rides on the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of the data that is gathered. Two words that are used repeatedly in the arena of clinical data management are Case Report Form (CRF) and Electronic Data Capture (EDC). Even though they are closely interrelated and often paired in usage, their purposes and functions are essentially different.
This article dissects the difference between CRF and EDC, describes each of their roles in clinical research individually, and illustrates how they complement each other to provide a seamless execution of clinical studies. We will also discuss how integrated platforms, such as Octalsoft's, are reshaping the manner in which CROs and sponsors handle clinical trial data management.
What is a Case Report Form (CRF)?
A Case Report Form, or CRF, is a formalized tool that is utilized in clinical trials to gather information from every participant. It is a formatted template used as a standard form to ensure that information required is collected repeatedly and as per the study protocol.
CRFs are study-specific and can contain fields for demographic information, medical history, laboratory results, adverse events, and outcome of treatment. Historically, CRFs existed in paper form, but increasingly, they exist in electronic forms as the industry moves toward more streamlined, technology-based processes.
The CRF is mainly used to obtain data needed for clinical trial protocol. When completed, the CRF is included in the official data set of the trial, which later may be utilized for regulatory submission, statistical analyses, and publication.
What is Electronic Data Capture (EDC)?
Electronic Data Capture (EDC) is the electronic system or software for collecting, storing, and processing clinical trial data in electronic form. Instead of marking up CRFs on paper, site staff enter participant data directly into the EDC system through a secure web application or interface.
EDC systems are designed specifically for clinical research and have many benefits compared to standard data gathering methods. These platforms generally have features of data validation, edit checks, query management, audit trails, and regulatory compliance.
EDC platforms provide increased control by trial sponsors, CROs, and regulatory agencies, allow real-time visibility into the data, allow quick decision-making, and minimize manual errors by making processes more efficient.
Key Differences Between CRF and EDC
Though CRF and EDC go hand in hand, they are not mutually interchangeable. They play different roles:
- CRF is the "what" — what you're going to collect.
It is the form or template that is used to collect clinical data. Regardless of whether it's on paper or via computer, it has pre-created fields into which certain bits of participant information are entered. - EDC is the "how" — the platform on which the data is gathered.
It's the system or tool that electronically records the CRF and enables data entry, management, and analysis in a secure, regulatory-compliant way.
Put simply, the CRF dictates what data is gathered, and the EDC system is the vehicle by which that data is captured, validated, stored, and retrieved.
The Evolution from Paper CRFs to EDC Systems
Historically, CRFs were nearly all paper-based. They were manually filled out by site personnel and couriered to data management organizations for entry into a master database. This was time-consuming, prone to errors, and costly, and frequently resulted in discrepancies in the data and delays.
With the advent of EDC systems, CRFs are also moved from paper to electronic ones. Electronic CRFs — simply eCRFs these days — are incorporated into the EDC platform. Site staff can enter the data directly into the system, which also automatically validates for errors, missing information, or inconsistencies.
This shift not only enhances data quality but also speeds up timelines, lowers costs, and supports compliance with regulatory requirements such as 21 CFR Part 11 and GCP (Good Clinical Practice).
How CRF and EDC Work Together
CRFs are designed in the protocol development stage of a contemporary clinical trial environment and subsequently set up within the EDC system. The EDC platform houses the electronic forms of the CRFs with built-in checks and controls based on logic.
When a study participant signs up for a study, investigators enter their information into the electronic CRF through the EDC system. This facilitates real-time data collection and monitoring, allowing centralized monitoring and faster resolution of issues.
The combination of CRF design and EDC implementation ultimately determines the quality, speed, and integrity of clinical trial data collection.
Advantages of the Use of EDC with eCRFs
The embedding of CRFs into an EDC system provides a number of benefits:
- Enhanced Data Quality: Edit checks and logic controls integrated within reduce the likelihood of data entry mistakes and inconsistencies.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Sponsors and CROs have access to view data entered in real time, enabling timely decision-making and quicker resolution of discrepancies.
- Regulatory Compliance: EDC systems are built to comply with regulatory standards, and audit trails, user access, as well as data integrity are ensured.
- Operational Efficiency: Automation of queries, validation, and reporting saves time and decreases the administrative load on sites and data managers.
- Scalability: Scalable and flexible, EDC systems accommodate small Phase I trials as well as large-scale global Phase III trials involving thousands of patients.
In Summation
The difference between CRF and EDC is their function: CRFs determine what information is required, whereas EDC systems determine how that data is gathered and stored. As the clinical trial landscape further adopts digitalization, the harmony among these aspects becomes increasingly critical.
Employing paper CRFs in a digital age not only impinges on clinical procedures but also poses the threat of data inaccuracy and regulatory non-compliance. EDC systems, with built-in eCRFs, are the way of the future for clinical data capture—faster, cleaner, and more efficient.
Whether you're building your initial clinical trial or refining a worldwide portfolio, grasping this core distinction can guide you towards wiser choices with respect to tools, processes, and platforms. And if you want a reliable, one-stop solution, Octalsoft's integrated eClinical platform provides the technology and assistance you require to speed success.
Selecting the Right EDC Platform: Why Octalsoft Excels
In the rapidly evolving clinical research world of today, the question of technology platform can have a profound influence on trial success. Octalsoft's Unified eClinical Platform is specifically designed to simplify the entire clinical trial life cycle — from protocol development and eCRF design to real-time monitoring and ultimate database lock.
What differentiates Octalsoft is its all-integrated solution, bringing together:
- Customizable EDC with easy-to-use eCRF design
- Randomization and Trial Supply Management (RTSM)
- ePRO/eCOA solutions for collecting patient-reported outcomes
- Integrated CTMS for trial management and operations
- Real-time insights and KPIs through analytics dashboards
Octalsoft's platform is secure, scalable, and fully compliant with all global regulations, providing seamless experience to sponsors, CROs, and research sites.
Ready to transform your clinical data management?
Related Blogs:
What is EDC in Clinical Trials?
How Electronic Data Capture (EDC) Can Improve Outcomes in Clinical Trials